Augmenting Remote Patient Monitoring with Artificial Intelligence of Things

Whether you are running, walking, exercising, or sleeping, these activities can improve your health. For patients suffering from a critical ailment or who have gone through a surgical procedure recently, monitor how these activities are impacting you and keeping track of vitals like heart rate or body temperature becomes important. However, understanding these metrics can be difficult for people without formal medical training. But what if a doctor could keep tabs on your activities and vitals while making suggestions to improve your health? This is what remote patient monitoring (RPM) allows health practitioners to do when they are connected to IoT devices that patients wear to measure movements and vitals.
Since the beginning of the pandemic, RPM has gained the attention of many healthcare experts because of these promises and recently IoT enabled monitoring devices to have emerged that are adding more capacities to RPM. In a previous article, we have already talked about the benefits of RPM in healthcare and briefly introduced the idea of IoT in RPM with our feature on holistic hospitals.
A doctor using an IoT enabled RPM system is more helpful to patients. However, a doctor may be managing the symptoms of many patients at one time which can be tedious and confusing. During the COVID pandemic, an artificial intelligence model was proposed to run on patient devices to detect asymptomatic infections. The system used pre-recorded sound data of patients and compared specific features of the speech signals of patients for this. AI in combination with IoT (AIoT) and RPM can help healthcare organizations and practitioners deliver better services to patients and opportunities to improve health outcomes.
Detecting Health Problems with Problems AIoT
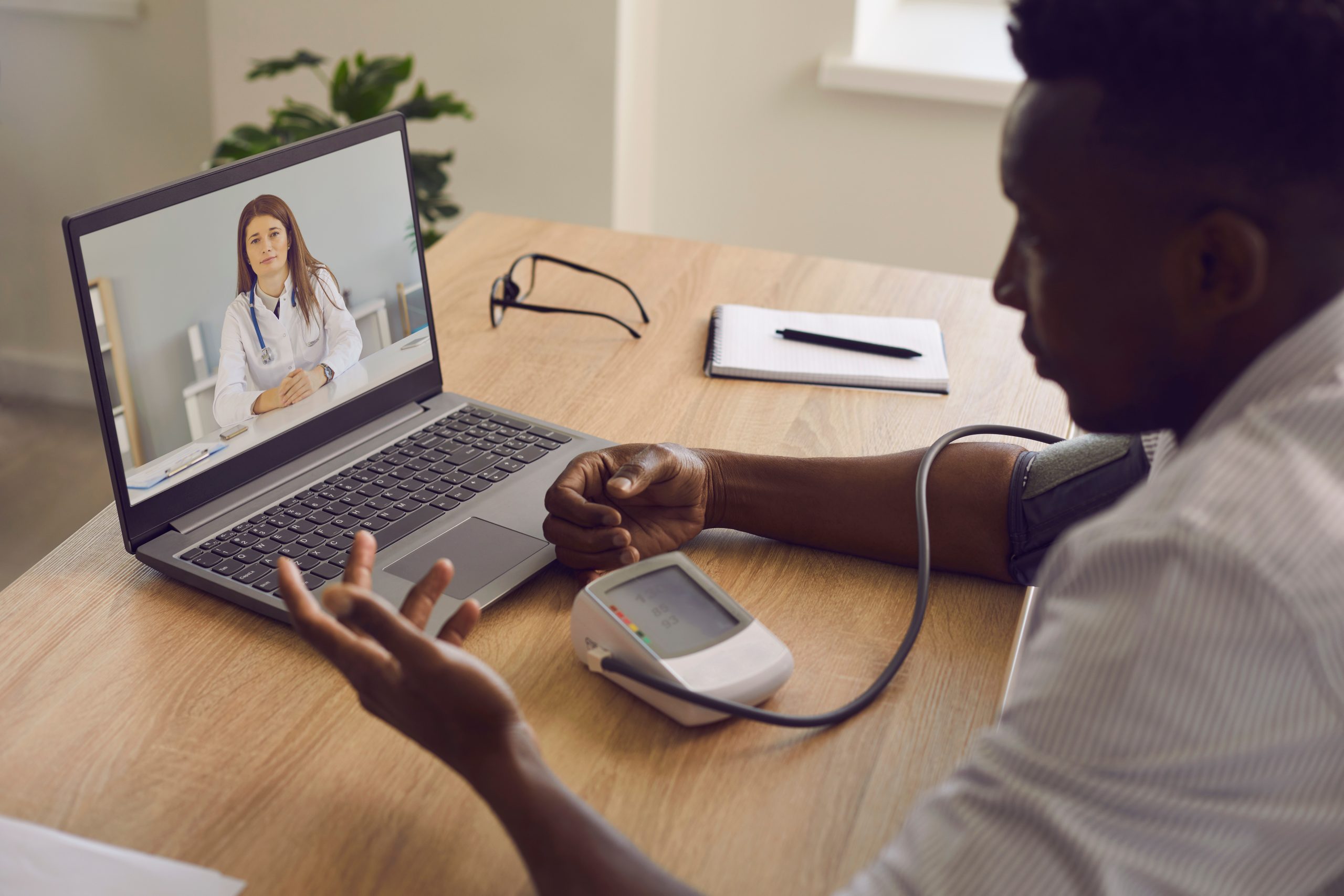
A regularly used smartphone can be turned into a health detection device that communicates with the health practitioner to enable support. An Android smartphone equipped with an accelerometer can be used to detect if a patient fell using the camera feature and the status can directly inform the practitioner as alerts through RPM.
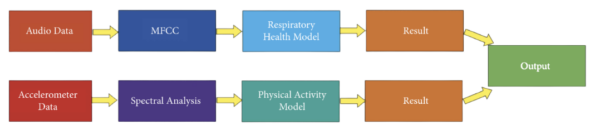
A healthcare organization developed a respiratory health model using audio data of patients with respiratory issues and compared it with the spectral analysis of the accelerometer data about the patient’s physical activity to help detect the possibilities of respiratory problems in a patient.
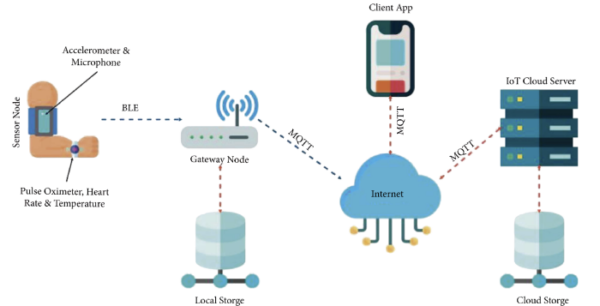
With AToT, doctors could find the diagnostics of the patient’s condition on real-time dashboards that provided a comprehensive view of health parameters and delivered intelligent health analysis reports. These reports were created with AI using the data on heart rate, oxygen levels, and body temperature obtained in real time from the patients through IoT sensor devices. Through built-in Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE) in devices, even patients remained updated with the latest data on health readings.
Intelligent Patient Monitoring
What if a patient suffering from a chronic disease is at risk of developing complications? How long will the patient take to realize it? Will the doctor be able to prevent the complication from developing or would they only be able to start the treatment when the complication has already occurred?
In most cases, the latter scenario is the most common. However, with the integration of AI and IoT in RPM, the former is also possible. Through the IoT devices used by patients, vitals like heart rate, oxygen level, or blood pressure can be read and shared with healthcare organizations. Normally, this data would go to a practitioner in the form of raw reports that have to be studied to sense the possibilities of complications. But with AI, predictions can be made about the possibility of complications through analytics. The result is proactive intervention from the healthcare practitioner that prevents the condition of the patient from growing worse.
The data collected through RPM such as carbohydrate intake, insulin, and other metadata can be fed into a machine learning (ML) program to analyze and identify patterns and predict abnormal conditions. For instance, if a patient is observed to have taken high-carb food items, has high glucose reading, and has not done much physical activity, this can hint at a possible complication that could develop in the near future. AI can act as an assistant to a doctor to help not just in detecting potential complications but also in deciding the line of treatment with the health data.
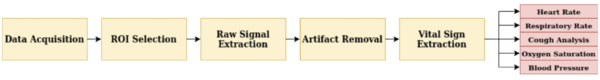
Figure 1: Remote Screen Process
Typically, AI in Remote Patient Monitoring can help monitor changes in the health of a patient, provide assistance to doctors on patient health outcomes, enable self-reporting from the patients, and integrate health metrics into clinical workflows. Some of the applications are:
- Contactless Screening
AI was also used at the time of the recent COVID epidemic for contactless screening during remote monitoring of those suspected of infection. Using a camera, vitals like respiratory rate, oxygen saturation, cough, temperature, and blood pressure were monitored. These vital signs could become the first observation that helped estimate the presence of SARS-CoV-2 in the body. Video-based diagnosis using AI can help in the early screening of diseases that are easily transmitted. Contactless screening like this can also be used to perform X-rays and MMRI scans. With ML algorithms, the data obtained can also be analyzed and the output can help doctors devise treatments or prescriptions.
- Clinical Trials
AI can be used for monitoring patient data remotely for clinical trials to capture physiological data such as blood pressure, blood oxygen, heart rate, respiration rate, and ECG from trial participants. ML algorithms like Artificial Neural Network (ANN) and Support Vector Machine (SVM) can help classify this data and make predictions abnormalities in the trial participants. The outcome of this analysis is usually presented in a human-readable format through dashboard visualizations.
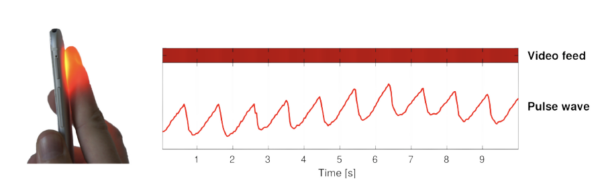
Figure 2: Photoplethysmography (PPG) technique
- Remote Monitoring of Heart Patients
Changes in the color of blood vessels can indicate problems as they are caused by motion variances of the heartbeats. Vision-based monitoring of the heart is possible with remote capture of Photoplethysmography (rPPG) signals that are radiated from the skin that reflects different specular shades depending on the blood color. Palm or fingerprint readings can also be used to calculate blood volume pulse (BVP) based on the reflection of light.
Augmenting Remote Patient Monitoring for Intelligent Healthcare
AI solutions can be used with IoT-enabled RPM for heart monitoring, respiratory monitoring, intelligent implants, contactless screening, clinical trials, and much more. With clear benefits of assistance to healthcare practitioners in the diagnosis, treatment, and care delivery, AIoT can improve healthcare outcomes for patients as well. In the near future, its application landscape will only expand to more areas of healthcare.
Apexon offers full-stack IoT engineering and development services to build the right IoT technology stack and data-rich software solutions for personal devices, medtech products, and beyond. Our domain experience in the healthcare and life science industry enables us to craft more efficient, innovative, and modern patient and provider experiences.




