Making Your Organization More Resilient to Cyber Attacks

In 2021, the average number of cyberattacks increased by 15.1% from the previous year. Executives polled by ThoughtLab predict a rise in attacks over the next two years as cybercriminals become more sophisticated. The main causes of these attacks are expected to come from misconfigurations, human error, and poor maintenance.
Organizations cannot fight these attacks simply by putting pressure on the IT teams to take preventive measures. Cyber security resilience must be built around people, processes, and technology. People must be aware, processes must be compliant, and technology can be used to support preventive measures. This article highlights ways to build resilience against cyberattacks by covering the following concepts:
- Impact of cybersecurity threats on organizations
- People’s impact on cybersecurity
- Security standards and compliances
- Establish procedures to strengthen security posture
- Tools for cybersecurity
Impact of Cybersecurity Threats on Organizations
In 2013, a cookie-based attack compromised over 3 million Yahoo accounts at the time when the company was going through negotiations with Verizon. The breach cost the company $300,000 in ransom and cut down the Verizon offer price by $350 million.
NotPetya, an encrypting malware, globally attacked many companies in 2017, causing a loss of over $10 billion that included $300 million to AP Moller-Maersk, $400 million to FedEx, and $870 million to Merck. The malware destroyed 3,500 servers of the logistics leader Merck which runs cargos covering almost a fifth of the world’s shipping capacity.
Cyberattacks are now common, and breach attempts are made every day to penetrate the defense systems of organizations. It is not just the frequency of attacks rising but also the variations in attack vectors that exploit your vulnerabilities. Even if your organization has assessed your systems for vulnerability and found no issues, your organization is not future-proofed.
Most small and mid-size companies implement bare minimum-security defenses and then take the reactive approach to demystify cyber forces when they attack. The result is damaging due to cyberattacks costing $6 trillion to organizations across the globe. In the next three years, the losses might cross the mark of $10.5 trillion, suggests Cybercrime Magazine.
On the other hand, preventive measures can avert 94% of the attacks. To develop the proactive cybersecurity landscape, an organization needs to take measures considering people, processes, and technologies. People can help prevent mistakes that can expose systems to intruders, processes can help streamline security measures, and technological tools can automate and simplify processes to strengthen the cybersecurity posture of an organization.
People’s impact on cybersecurity
Many organizations today use VPN services to secure their network so that they can encrypt user access to their corporate network. An employee of Colonial Pipeline did the same on this company computer in 2014. He connected to the VPN from a location other than his office. This created an opportunity for DarkSide, a Criminal Hacker group from eastern Europe, to steal 100 gigabytes of data from the company’s billing system.
This caused a panic in America’s largest petroleum pipeline, and about half of the pipeline on the east coast was shut down for a couple of days. As a result, 15.4% of fuel stations in Georgia and 60% in Atlanta went dry. The consumer price for one gallon of gas rose from $2.927 to $3.008 because of shortages across states. A threat message was then floated asking the company for a ransom amount of $5 million or the stolen data would be released on the internet. Unfortunately, the company had no choice but to pay the amount in exchange for a decryption tool.
As per statistics, 95% of the security breaches are caused by human errors or lack of awareness as attackers use social engineering tactics like phishing to manipulate users into performing dangerous actions they desire. Among the breaches faced by SMBs, the most frequent is a phishing attack that accounts for 90% of breaches. Thus, it is essential for people to understand cybersecurity risks and the impacts of their actions to prevent such breaches.
One small mistake by one ignorant employee can cost millions to an organization. However, an employee aware of security protocols would know what not to do to create an opportunity for attackers. Cybersecurity awareness among your employees is not a choice but a necessity for your organization because attackers are waiting to capitalize on the ignorance of your employees.
At Apexon, we leverage a Cyber Security Awareness Platform, a leading training tool in the segment. The training catalog covers a variety of cybersecurity features like Phishing Campaign, Automated Security Awareness Program, Vishing module, Second Chance, and Modstore. The tool has helped us cover users across all locations, which was challenging to do with manual training. The platform was used to run phishing campaigns to train users on various cybersecurity modules.
A layer of discussion is created between IT and functional teams to help employees learn about cybersecurity with quizzes created to test their awareness. The employees receive user digest on email activities, announcements of the latest developments or events in cybersecurity, and updates on measures taken by the company to strengthen security.
A typical update would look like:

The Apexon IT team continuously monitors all activities, and any deviation from activities, whether harmful or not, is flagged and clarified through a personal connection that ensures that employees understand how their actions can affect the organization. All emails are assigned priorities based on their categories. Emails low on priority are flagged, quarantined, and individual users are automatically informed about taking a final action to block or retain.
Security Standards and Compliances for Cybersecurity
Cybersecurity aims to protect organizational systems, devices, programs, and networks from unauthorized usage by cyber attackers. It is not a one-time step to take but a process that involves identification of threats, protection from unauthorized users, detection of attacks, responding to attacks, and taking measures to recover from a breach. When you have the proper process in place, you can be proactive and minimize breaches. This would mean you could save millions of dollars with preventive cybersecurity measures.
You need to know your current security posture and where you stand when considering cybersecurity procedures. For this, ask your IT teams:
- Is your organization compliant with security standards and has a process to monitor and maintain cybersecurity?
- Do you have a defined cybersecurity policy that identifies ways to prevent and deal with security breaches?
- Do the policy measures have consideration of both humans and machines?
- Does your policy cover the processes, safeguards, and techniques in all significant areas of cybersecurity?
NIST has identified 22 categories of processes, safeguards, and techniques under the five functional areas of cybersecurity:
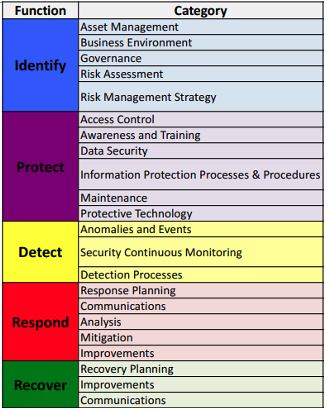
Figure 1: NIST Classification
Preventive measures are covered in the first three functions of the cybersecurity framework – Identify, Protect, and Detect. Let us see what processes and techniques support these functions.
Identify: To start with cybersecurity measures, your first step is identifying which assets, processes, and people need protection. Assets include data, devices, systems, and facilities managed by an organization. Processes include management and monitoring of the organization’s operational, legal, regulatory, and environmental requirements. People include stakeholders of the organization whose roles and responsibilities related to cybersecurity have to be determined. A risk assessment is done at this stage to understand risks, and a risk management strategy is developed to establish assumptions, priorities, constraints, and tolerances.
Protect: Key protection measures an organization can take to prevent security attacks and breaches include access control mechanisms, training and awareness programs, data security measures to protect confidentiality, integrity, and availability of data, security policies, maintenance procedures, and protective technologies.
Detect: Once protection measures are in place, an organization needs to continuously monitor systems and assets to check for the effectiveness of protective measures. It also involves the detection of anomalies occurring in data or processes. Timely detection of anomalies is essential to minimize or mitigate the impacts of security breaches.
Tools for Cybersecurity
In 2017, WannaCry Ransomware affected 230,000 computers across the globe in more than 200,000 organizations from 150 countries. The attack affected a third of NHS hospital trusts, costing them £92 million. In NHS England, 80 trusts, 603 primary care units, and 595 General Practices were affected. However, this was not the limited damage. WannaCry affected organizations across the globe, including FedEx in the US, Renault in France, and MegaFon in Russia. The attacker began by exploiting a vulnerability in a single Microsoft computer system. Then the infected program would be copied and executed across the systems connected in a corporate network.
A vulnerability could be in your machine or in an application you are using, but the ripple effects of it will make many organizations suffer. Thus, it is a prerogative of an organization to prevent its technological systems from being attacked by securing vulnerabilities that can cause damage.
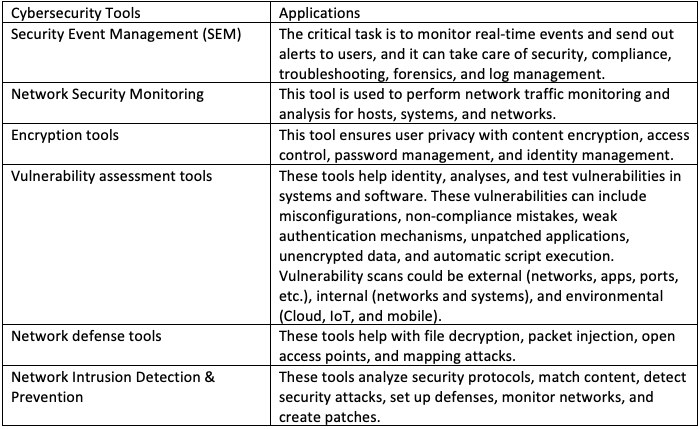
While on one side, technology is exploited by attackers, on the other side, engineers who counter these attacks also offer tools to help us monitor, predict, and analyze our systems to reduce the chances of attacks on us. Many useful cybersecurity tools are available for network security monitoring, encryption, vulnerability scanning, penetration testing, auditing, network intrusion detection, incident response, security event management, and malware detection.
Putting it Together for Resilience Against Cyberattacks
People, process, and technology – when they go together, you can strengthen your security posture and take preventive measures on time to prevent most security attacks, saving millions of dollars. Cybersecurity is not a one-and-done solution, but it needs a continuous program that keeps improving the security posture of an organization. You can’t trust mechanisms because attackers adapt. You can’t trust people as they make mistakes. The only savior is to keep working and refining together.
Apexon’s Security Testing services uncover security vulnerabilities and ensure minimal security risks. We offer end-to-end security testing services to protect your applications from cyber vulnerabilities at every stage of software development and maintenance. Apexon leverages the latest tools and techniques to enable the best possible use of resources and time to make the security testing process streamlined and manageable.
To learn more, check out Apexon’s Security Testing services.
