RPA vs Traditional Automation: Which is Better and Why

This article was cowritten by Umakanthan SN, Gurumurthy Kalyanaraman, and Raghavendra Vishnukumar Gattewar
Understanding the differences, types of automation, how it fits into your workflows, and your organization’s adoption readiness are the keys to unlocking positive business outcomes.
The Big Idea: Automation helps organizations make better use of their time and resources. This article will examine the difference between traditional automation, robotic process automation (RPA,) and Intelligent Automation (IA), and serve as guidance to support their decisions around the adoption of RPA.
Why is it important: Automation helps companies save time, energy, and investments. They can ease the lives of their employees, improve customer satisfaction, and bring efficiency to organizations. Finding the right automation solution will help you unlock these benefits.
What’s ahead:
- Traditional automation vs RPA vs IA
- Benefits of RPA
- RPA use cases
- RPA FAQ
- RPA readiness assessment
- Future of Automation
Automation at a Glance
Despite their name, modern knowledge workers aren’t always using knowledge to do their jobs. In fact, a large part of work done in the workplace doesn’t require much thinking at all.
- Around 35% of an average workload is repetitive and mundane
- Over 40% of workers surveyed spend at least a quarter of their work week on manual, repetitive tasks
- For a US organization with 500 people, the annual financial loss because of repetitive tasks can be over $1.47 million
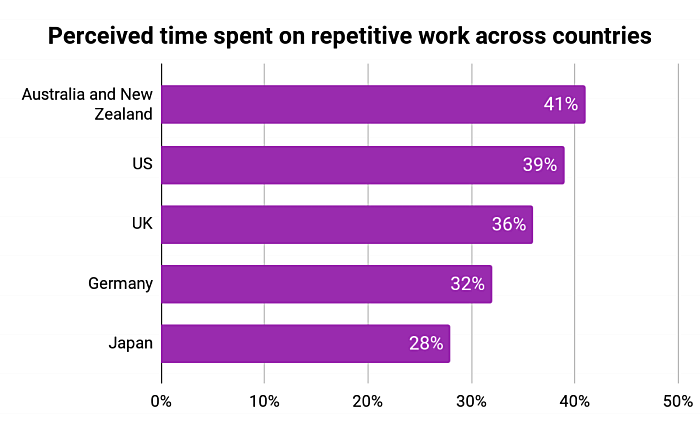
The advent of automation brought a solution to this plague of thoughtless, mundane work. Automation first found its roots in manufacturing with the advent of transistors, motors, and industrial control systems that speed up assembly lines. It later reached the services sector with systems like Automated Teller Machines (ATMs). Today, several forms of automation are available, all with different characteristics and capabilities.
Traditional Automation vs RPA vs Intelligent Automation
Traditional automation is the automation of repeated tasks with minimal human intervention, using APIs and programming to integrate different systems.
Traditional automation programs were designed to integrate user applications with the backend systems of organizations to autonomously perform pre-defined tasks without the need for human intervention.
Traditional automation made its way into the service industry, majorly with applications in customer service and workflow automation areas. Desk booking, user service ticket submissions, and troubleshooting are standard customer service processes that are automated. Workflow automation examples are an aggregation of analytics, extensive collection, and asset relocation.
However, traditional automation has limitations. Traditional automation systems are limited by the capacities of programmers to embed instructions in their codes. Traditional automation can only run tasks as per the stored procedures because traditional automation systems are not intelligent enough to adapt or learn on the job. Thus, humans must often intervene in traditional automation workflows to make modifications.
Robotic Process Automation embeds human intelligence in software bots, allowing them to quickly learn and adapt with every task. RPA is fast, easy, more adaptable, has no dependencies, and has a short learning curve for users. Moreover, RPA can handle more complexities with less effort than traditional automation procedures.
RPA is a platform-agnostic approach that can be used to automate any process or part of any application on any platform. Whether it is your mainframe, desktop, web, or mobile application, RPA can embed automation in them with virtual machines that have no limitations of storage or bandwidth. What traditional automation would take months to build, RPA can flip within days. Moreover, there are no challenges of compatibility or limitations of APIs as robots are directly imitating humans and learning from users.
Advantages of RPA over traditional automation are vast, and those topping the list are
- Ease of integration
- Less implementation times
- Higher scalability
- High level of customization
- Cost-saving virtual machines
- Streamlined processes improve accuracy
Intelligent Automation (IA) goes a step further by combining RPA with advanced technologies such as artificial intelligence (AI), analytics, optical character recognition (OCR), intelligent character recognition (ICR), and process mining to create robust business processes that learn and adapt on their own. Intelligent automation is sometimes referred to as intelligent process automation (IPA) and hyper-automation. IA comes into play after RPA has been implemented and is part of a long-term digital transformation strategy.
RPA FAQ
Below are some common questions business users ask prior to RPA adoption:
Is RPA only beneficial to large companies?
Regardless of size, RPA can help automate processes and save 35% of your workforce hours, giving people more time to focus on growth and create competitive business value.
What are some benefits of RPA?
Organizations adopting RPA have experienced benefits in many areas of their operations.
- A Global Survey by Deloitte reported that 92% of the organizations adopting RPA had observed improvements in compliance, 90% of them improved accuracy, and 86% enhanced productivity
- A global healthcare company in over 100 countries saved significant person-hours by automating 140 processes with 200 software bots
- A national bank brought down the error rates in their 2 million daily transactions to nearly zero with RPA
- A consulting giant released 25% of the capacity of their operations staff with RPA implementation
What will be the ROI from RPA?
RPA has helped companies gain cost savings between 20% to 60% in financial services. By 2025, Hadoop researchers estimate a saving of up to $7 trillion for companies globally with RPA.
Industry RPA Use Cases
Rule-based, repetitive tasks exist in all verticals. RPA is extremely prevalent in the banking, financial services, and insurance industry as well as healthcare.
RPA in Insurance: The insurance value chain is long and consists of many repetitive tasks like:
- Invoicing
- Underwriting
- Policy issuance
- Policy renewal
- Claims processing
- Adjudication
- Reporting
A typical renewal process of a global insurance company would use over 25 applications, involve several non-standardized processes, and exchange numerous documents and emails. With RPA, it can speed up customer response time, improve accuracy, reduce full time equivalent headcounts, and increase efficiency.
RPA in Banking and Financial Services: In banking, digital transformation is fueled by RPA that automates tedious banking processes like new account opening, credit card processing, mortgage processing, and fraud detection. Apexon helped a large bank improve their operational efficiency by 15% and save 25,000 hours of rework by implementing RPA. Here are a few more use cases of RPA in the BFSI sector:
- Trade finance operations
- Customer onboarding
- Anti-money laundering (AML)
- Accounts payable
- Credit card processing
- Loan application processing
- General ledger
RPA in Healthcare: As per McKinsey Global Institute, healthcare presents 40% potential for automation and can solve significant problems for healthcare facilities like an aging workforces, inflexibility in legacy systems, and increasing costs. Hospitals and other healthcare organizations use RPA to automate their manual workflows, including:
- Billing
- Enrollments
- Claims management
- Claims processing
- Authorization
- Appointment scheduling
- Record management
Are You Ready for RPA Adoption?
To understand if an organization is ready for RPA, four processes must be conducted:
- Needs assessment
- Impact analysis
- Feasibility analysis
- Complexity assessments
1. Needs Assessment: What processes are good candidates for automation? How labor-intensive and repetitive are your processes? What is the percentage of tasks that can be automated?
Some checkpoints to identify the right candidates for RPA are:
- High rate of transaction of the process
- Standardized and rule-based process
- Predictable cost of operations
- Less variation in scenarios
- Standard and readable inputs
- Methodologies are not subject to change
2. Impact Analysis: To what extent will automation affect the business focus areas? To what extent will RPA contribute to their achievement? How will it affect the efficiency and productivity of the processes?
Several process attributes can be reviewed for impact assessments, such as:
- Does the process follow stringent rules?
- Can the process be judged independently by an individual?
- Is the process currently manual and highly repetitive?
- Is the data involved primarily structured and can it be easily analyzed digitally?
- Are the inputs digitized and can they be read easily using computer systems?
- Is the process prone to human errors that can it be reduced with RPA?
- Is the skill required to perform the task easily transferable?
- Can we easily measure the positive or negative effects of automation?
3. Feasibility Analysis: This step will help you determine if your processes and/or RPA strategy are realistic.
A few questions to ask yourself are:
- Are the identified processes repetitive and follow specific rules?
- Do they have clearly defined input, execution steps, and output?
4. Complexity Assessment: This step can be defined by the number of applications involved, frequency of human intervention, steps required to complete a task, etc. Determining the ROI of your RPA project is also included in the complexity assessment.
The Future of RPA
Hadoop has estimated that by 2025, organizations will save up to $7 trillion with RPA implementations. No wonder RPA adoption is on a rapid rise; by 2027, the RPA market is expected to grow to $25.56 billion.
As RPA is growing its footprints in the business world, we’ll start to see more sophistication with automation, including IA or hyper-automation. Hyper-automation is the future of RPA. It not only allows automation of repetitive tasks but also facilitates adaptation and intelligence to support improvements and decision-making. It brings predictive insights, intelligent recommendations, and adaptive decision-making to help organizations in digital transformation. Are you ready to automate?
To help us assist you in assessing your company’s readiness for RPA, check out Apexon’s Intelligent Automation Services or get in touch directly using the form below.



![5 Ways Automation Humanizes the Workplace [Plus 1 Bonus]](https://s40886.pcdn.co/wp-content/uploads/2022/06/AdobeStock_411736181-scaled-1.jpeg)
