The challenge is to make your application work and work well across this constantly evolving ecosystem.
This means quality mobile app development needs:
Implementing the optimal mobile testing strategy
The mobile market is booming, the app economy is exploding and the need for mobile testing continues to grow. But mobile testing is very different from traditional enterprise, web and packaged application testing. There are various devices with numerous form factors, fast changing mobile OSs, and growing demand to support mobile applications globally.
Each phase of mobile quality brings its own set of unique challenges to be addressed. For example, in Planning, there needs to be a focus on device selection. In Definition, specific types of tests and processes need to be well defined. In Execution, remote access and conditioning issues for devices need to be covered. With Automation, users have to account for ROI, tools, types of test cases, etc. And in the last phase of mobile quality, Optimization, post release support and upgrades need to be measured and addressed.
To do all this, the overall testing strategy needs to be well defined with the right tools, framework and technology. This white paper discusses the different considerations for mobile testing and lays out a blueprint for creating an optimal mobile testing strategy with risk mitigation plans and streamlined processes.
The challenge is to make your application work and work well across this constantly evolving ecosystem.
This means quality mobile app development needs:
The mobile landscape is changing real time – new devices, new versions of operating systems, new carriers and of course, new applications.
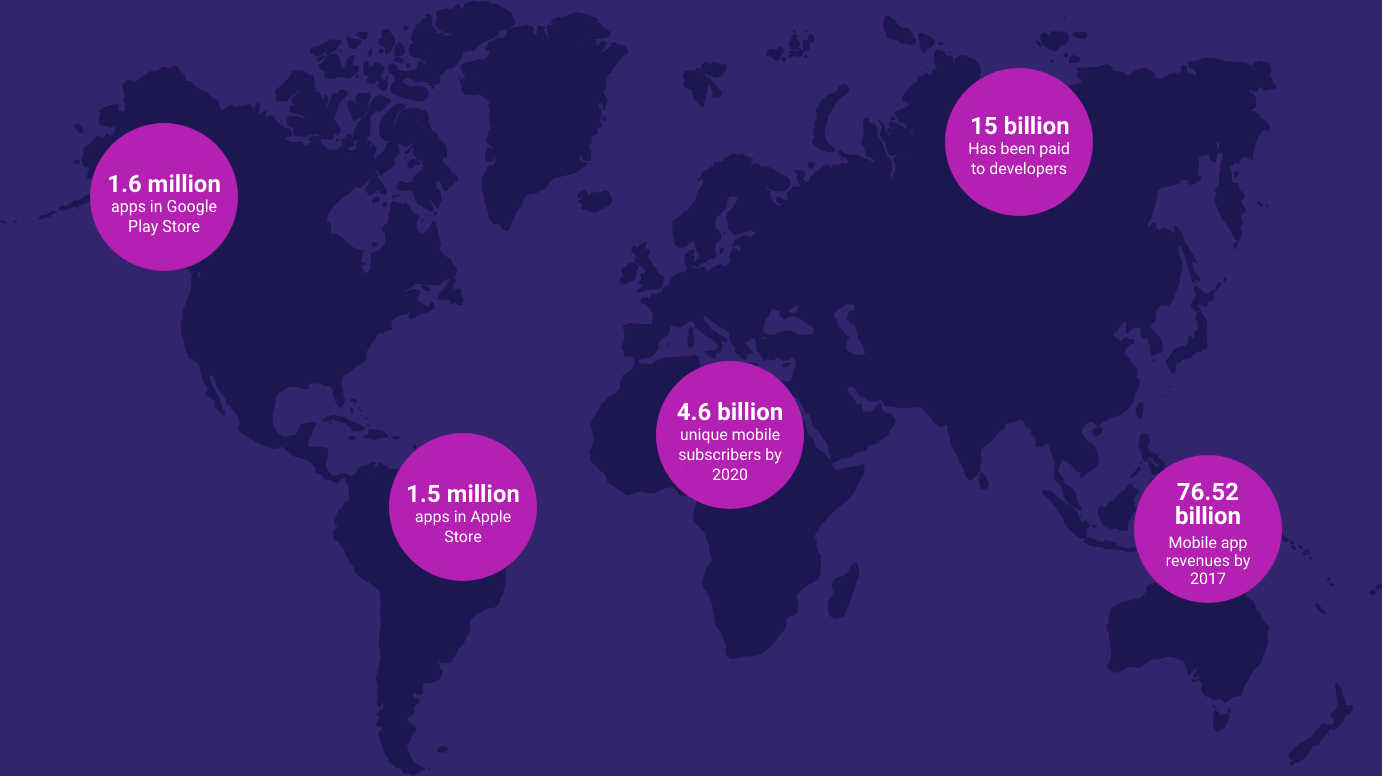
Mobile testing is different from traditional enterprise QA. With a zillion device / OS combinations challenging testing coverage, security issues, and varied device connection speeds impacting application performance, mobile testing quickly becomes the largest elephant in the room.
Apart from adding device provisioning and device level validations, there are issues related to memory, network bandwidth, cross platform, screen size and resolution compatibility. There are functional issues related to swipes, UI and localization. There are security concerns such as caching, uploading personal information to servers, virus scanning, memory corruption and more. All this makes mobile QA a very different animal.

Interaction with Device/OS native capabilities
Optimal combination of devices and OSs
Effective combination of manual and automated testing
Need for faster agile adoption
On-time and off-line connectivity
The best QA strategy to test a mobile app depends on the type of app. If it is a native app, then there are certain conditions which need to be tested.
The tester needs to ensure that the app can be successfully downloaded, executes on the device and interacts with the backend infrastructure. Apps render differently across devices, so each app needs to be thoroughly tested on all relevant devices. We must also ensure backward compatibility with selected older generation devices and OSs. Creating test plans for manual testing on each of these devices can be a cumbersome process.
Mobile web apps pose a different set of challenges. These apps are viewed by users across the globe, presenting unique challenges in terms of networks, scripting and devices. No matter what type of app it is – native, hybrid or web – manual testing of these apps has become more rampant. Testing on simulators does not accurately replicate real user experience. And, testing on all device/OS combination is not practical .The other issue that we have already touched on is the lack of a standardized mobile SDLC, which results in an inconsistent testing methodology.
Selecting the right mobile testing methodology is critical to the success of any mobile initiative. You need a partner who understands the intricate details and brings the required knowledge as well as the right infrastructure and enabling technology.

It’s imperative to link business goals and quality goals, leveraging key quality dimensions specific to mobile testing.
This means:
Define key policies, components, review criteria, approach, testing types, scope, communication and resource planning necessary to control and manage risks throughout the Software Testing Program.
Address key areas such as test approach, scope, test types, review criteria, test data, incident management, resources and supplementary materials.
Identify and outline key objectives of the test validation, related requirements and testable items. All required test pre-conditions and processing in detail with associated supplementary materials.
Provide dynamic snapshot of progress throughout the testing life cycle, providing visibility to management and stakeholders. The overall summary, scope deviation, requirements coverage, analysis/design progress, execution progress, review criteria and outstanding defects are areas that will be addressed throughout the life of the project for review, approval and sign-off.
Define repeatable process and help you streamline your testing to support on-demand releases and critical software changes. A hybrid automation framework is deployed for immediate use, eliminating development ramp-up time.
Provide a relational model of your software testing validation framework. Requirements and User Stories are mapped to Test Cases and Test Plan and are executed against target software build releases, configurations and environments.
Each of the test result is well supported with tester comments and screenshots along with the required logs for the developer to understand the issue, and be able to reproduce the same without any trouble.
Provide an overall review of the efficiency and effectiveness of testing activities. Assessment methodology uses interviews with key testing leaders and an analysis of your testing deliverables in a short time frame to provide recommendations.
There are different types of testing that need to be addressed – independent of the platform – to ensure mobile app quality. Following is a snapshot of the various testing types and test cases.
Because mobile testing must be performed on so many different combinations of devices, browsers, and operating systems, doing it manually quickly becomes impractical in terms of both time and expense. Test automation can bring significant efficiencies to the process – dramatically accelerating go to market plans and reducing costs.
The virtually endless combination of devices, OS models, and device sizes. Test automation enables QA teams to test the same functionality on different devices, OSs and form factors.
Constant OS updates, upgrades, new devices, and new manufacturers. In order to ensure that the application is up-to-date and supported by new trends, testing it in a timely manner becomes important.
Apps are regularly updated with new features in order to keep up with market demand. In order to introduce upgrades into the market quickly, automated testing is crucial.
It’s imperative to link business goals and quality goals, leveraging key quality dimensions specific to mobile testing.
This means:

Mobile testing can be complex but app quality is critical to success in today’s business world. The traditional rules of testing do not apply to mobile due to the fast changing landscape, unique features of apps and devices, limited bandwidth and unreliability of wireless networks.
There is a need to develop mobile specific test methodologies and guidelines and therefore a need to rely on a testing partner. This partner should be able to provide insights to modern approaches in testing and suggest the right QA strategy and coverage based on specific business needs.
After defining the qa strategy, your QA partner should provide a well-defined plan on what types of testing and what attributes need to be tested, validated and verified. Ideally, they would have executed testing strategies for enterprises across different verticals – retail, travel, banking and insurance, and digital entertainment – so they understand all the different possibilities and use case scenarios.
The ability to use the right combination of emulator and real device testing to ensure predictability; emulators with scripting help to test many aspects at an effective cost
The ability to provide intelligence behind use of select devices for your application
The ability to provide automation and agile solutions for faster time-to-market by building the right user stories, increasing use of test sprints and creating script reusability
The ability to have access to the real devices remotely when it’s not possible to run physical test on a slew of mobile devices
The ability to increase the app store star ratings of the app by closely monitoring it and providing reactive and proactive remediation
The ability to optimize the adoption and monetization of the application post-launch